Describe the Basic Structure of an Amino Acid
Metal oxides hydroxides and especially alkoxides are basic and conjugate bases of weak acids are weak bases. The amino acids differ in structure by the substituent on their side chains.
Indeed if one considers amino acids that possess much more basic NH 2 groups this is likely that a full protonation of the amino group might occurs in the presence of.
. Each nucleic acid consists of a number of basic building blocks called nucleotides. 1 phosphate ion 1 pentose sugar 1 nitrogenous base Nitrogenous bases are divided into two complementary groups. The subunits are held together by hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces between nonpolar side chains.
This will yield two pK values that occur on either sides of the isoelectric form A of amino acid. The structures of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins are shown in Figure 1. DNA forms a.
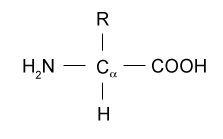
But many other amino acid changes are effectively neutral having neither a beneficial nor a damaging effect on the basic structure and function of the protein. Amine group central carbon carboxylic group and an R group. An amine group is a chemical group that.
The CuAAC process has emerged as the premier example of click chemistry a term coined in 2001 by Sharpless to describe a set of near-perfect bond-forming reactions useful for rapid assembly of molecules with desired function. The quaternary structure of a protein is the association of several protein chains or subunits into a closely packed arrangement. The structure of the amino acid histidine is.
The zinc ion is bound to these histidine rings via dative covalent co-ordinate covalent bonds from lone. Each of the subunits has its own primary secondary and tertiary structure. The subunits in a quaternary structure must be specifically arranged for.
Glutamic acid has the normal amino acid structure of an amino acid. 1 Click transformations are easy to perform give rise to their intended products in very high yields with little or no byproducts work well under. These side chains confer different chemical physical and structural properties to the final peptide or protein.
Each amino acid has both a one-letter and three-letter abbreviation. Dissociation of amino acid as occur in the dissociation of acidic and basic amino acids. In addition since mutation is a random process there must also have been many deleterious changes that altered the three-dimensional structure of these proteins sufficiently to harm them.
And when it is a part of a protein chain it is joined up like this. A reaction between aqueous solutions of an acid and a base is called. Where purines will.
If you look at the model of the arrangement around the zinc ion in the picture above you should at least be able to pick out the ring part of the three molecules. Bases and acids are seen as chemical opposites because the effect of an acid is to increase the hydronium H 3 O concentration in water whereas bases reduce this concentration. Each nucleotide consists of three parts.

General Structure Of A Amino Acid Download Scientific Diagram
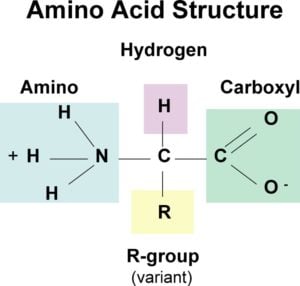
Amino Acids Definition Properties Structure Classification Functions

Amino Acids Structure Classification Properties With Videos Examples
No comments for "Describe the Basic Structure of an Amino Acid"
Post a Comment